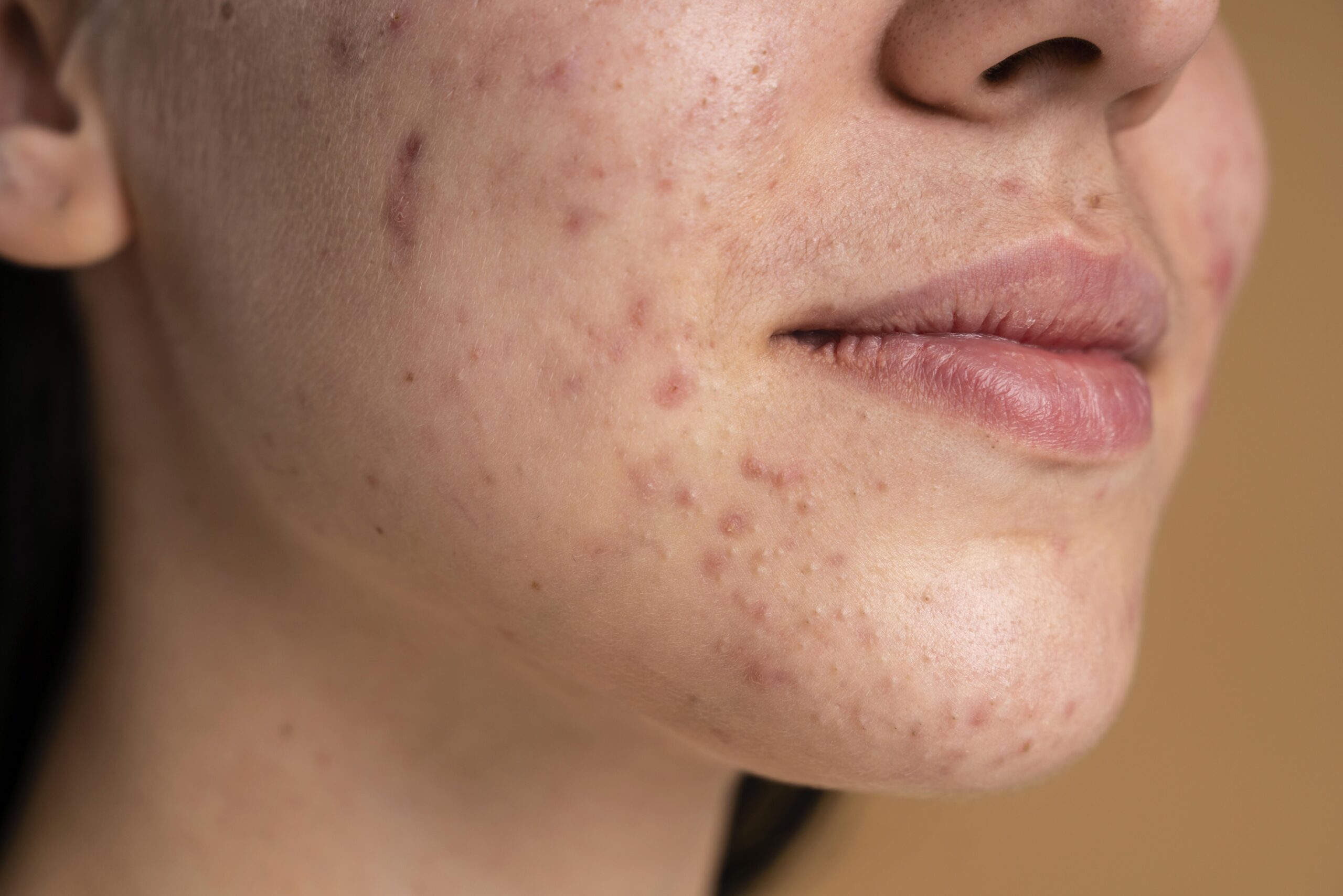
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by patches of skin that become darker than the surrounding areas. While it’s generally harmless, it can be a source of frustration and self-consciousness for many. This blog will delve into the causes, types, prevention, and treatment of hyperpigmentation to help you achieve a clearer, more even complexion.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, forms deposits in the skin. This can result in dark spots or patches that are darker than the surrounding skin. It’s important to note that hyperpigmentation can affect people of all skin types and tones.
Common Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Understanding the underlying causes of hyperpigmentation is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Here are some common causes:
- Sun Exposure: The most common cause of hyperpigmentation is sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) rays trigger an increase in melanin production as a natural defense mechanism, leading to sun spots or age spots.
- Inflammation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) can occur after skin inflammation or injury, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis. The skin produces extra melanin in response to the inflammation.
- Hormonal Changes: Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation often triggered by hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, birth control use, or hormone replacement therapy.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and anti-seizure drugs, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, including Addison’s disease and hemochromatosis, can cause hyperpigmentation.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can manifest in various forms, each with unique characteristics:
- Melasma: Often called the “mask of pregnancy,” melasma appears as brown or gray-brown patches, typically on the face. It is more common in women and is often linked to hormonal changes.
- Sun Spots: Also known as age spots or liver spots, these small, darkened areas usually appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): These dark spots develop after an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or cuts.
Prevention of Hyperpigmentation
Preventing hyperpigmentation involves protecting your skin from triggers and adopting a consistent skincare routine. Here are some preventive measures:
- Sun Protection: Wear sunscreen with a high SPF daily, even on cloudy days. Broad-spectrum sunscreens that protect against both UVA and UVB rays are ideal. Additionally, wear protective clothing and seek shade when the sun is strongest.
- Avoid Picking Skin: Avoid picking, squeezing, or scratching your skin, as this can lead to inflammation and PIH.
- Gentle Skincare: Use gentle skincare products to avoid irritating your skin. Look for products that are free of harsh chemicals and fragrances.
- Regular Exfoliation: Exfoliate regularly to remove dead skin cells and promote skin cell turnover. However, be careful not to over-exfoliate, as this can cause irritation and worsen hyperpigmentation.
Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
If you already have hyperpigmentation, several treatments can help reduce its appearance:
- Topical Treatments:
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production. It is often used in combination with other treatments.
- Retinoids: Promote cell turnover and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that can brighten skin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Niacinamide: Helps to lighten dark spots and improve skin texture.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin that causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off, revealing new, evenly pigmented skin underneath.
- Laser Treatments: Laser treatments target and break down melanin deposits in the skin, reducing the appearance of dark spots.
- Microdermabrasion: A minimally invasive procedure that exfoliates the skin, removing the outermost layer and reducing hyperpigmentation.
- Natural Remedies: Some natural ingredients, like aloe vera, licorice extract, and green tea, have skin-lightening properties and can be used as part of a skincare regimen.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation can be a challenging skin condition to manage, but with the right knowledge and tools, it is possible to reduce its appearance and prevent new spots from forming. Consistent sun protection, gentle skincare, and effective treatments can help you achieve a more even complexion. If you’re struggling with hyperpigmentation, consider consulting a dermatologist to determine the best course of action tailored to your skin’s needs.