Exfoliation is a critical step in any effective skincare routine, helping to remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and promote a smoother, more radiant complexion. Among the most popular exfoliating actives are Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs), Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs), and Polyhydroxy Acids (PHAs). These powerful ingredients offer distinct benefits and are suitable for various skin types and concerns. In this guide, we’ll explore the unique properties of AHAs, BHAs, and PHAs, and how to incorporate them into your skincare regimen for optimal results.
The Importance of Exfoliation
Exfoliation helps to remove the outer layer of dead skin cells, revealing fresher, healthier skin underneath. Regular exfoliation can improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, prevent acne, and enhance the absorption of other skincare products. Understanding the different types of exfoliating actives and their specific benefits can help you choose the right one for your skin type and concerns.
AHAs (Alpha Hydroxy Acids)
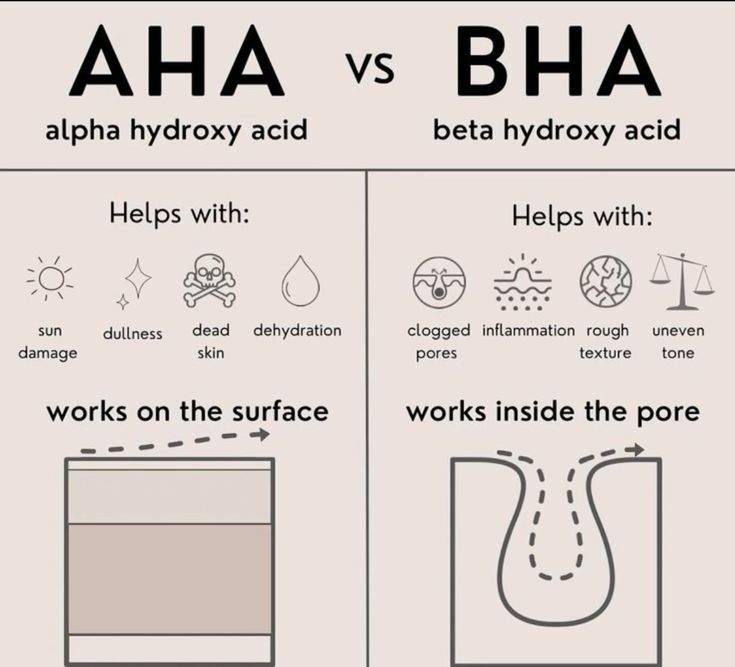
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) are water-soluble acids derived from various plant sources and milk. They work by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing them to be easily removed from the skin’s surface. AHAs are particularly effective for improving skin texture, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and addressing hyperpigmentation.
Common Types of AHAs:
- Glycolic Acid: Derived from sugar cane, glycolic acid has the smallest molecular size of all AHAs, allowing it to penetrate deeply into the skin. It is highly effective for exfoliating, brightening, and improving skin texture.
- Lactic Acid: Sourced from milk, lactic acid is a milder AHA that exfoliates while also providing hydration. It is suitable for sensitive skin and helps to improve skin tone and texture.
- Mandelic Acid: Extracted from bitter almonds, mandelic acid has a larger molecular size, making it gentler on the skin. It is excellent for treating hyperpigmentation and improving overall skin clarity.
Benefits of AHAs:
- Promote cell turnover for smoother, more radiant skin.
- Reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Improve skin texture and tone.
- Help fade dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Hydrate the skin by attracting moisture.
BHAs (Beta Hydroxy Acids)
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs) are oil-soluble acids that penetrate deep into the pores to exfoliate from within. This makes them particularly effective for treating acne-prone and oily skin types. BHAs help to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and control excess oil production.
Common Types of BHAs:
- Salicylic Acid: The most common BHA, salicylic acid is derived from willow bark. It penetrates deep into the pores to dissolve excess sebum and dead skin cells, making it highly effective for treating blackheads, whiteheads, and acne.
Benefits of BHAs:
- Exfoliate inside the pores to prevent and treat acne.
- Reduce excess oil production.
- Minimize the appearance of pores.
- Calm inflammation and redness.
- Improve overall skin texture.
PHAs (Polyhydroxy Acids)
Polyhydroxy Acids (PHAs) are a newer generation of exfoliating acids that offer similar benefits to AHAs but with less irritation. PHAs have a larger molecular structure, which slows their penetration into the skin and reduces the risk of irritation, making them ideal for sensitive skin types.
Common Types of PHAs:
- Gluconolactone: A gentle exfoliant that helps to remove dead skin cells, hydrate the skin, and provide antioxidant benefits.
- Lactobionic Acid: Derived from milk, lactobionic acid offers gentle exfoliation, hydration, and antioxidant protection.
Benefits of PHAs:
- Gently exfoliate without causing irritation.
- Provide hydration and improve skin barrier function.
- Offer antioxidant protection to combat free radical damage.
- Suitable for sensitive and reactive skin types.
- Help improve skin texture and tone.
Incorporating Exfoliating Actives into Your Routine
To get the most out of exfoliating actives, it’s important to incorporate them into your skincare routine correctly. Here are some tips:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to exfoliating acids, start with a lower concentration and gradually increase as your skin builds tolerance.
- Patch Test: Before using a new product, do a patch test to check for any adverse reactions.
- Use Sunscreen: Exfoliating acids can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, so always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation: Over-exfoliating can damage your skin barrier and lead to irritation. Use exfoliating products as directed, typically 2-3 times per week.
- Follow with Hydration: After exfoliating, follow with a hydrating serum or moisturizer to replenish moisture and soothe the skin.
Caution
When incorporating exfoliating actives like AHAs, BHAs, and PHAs into your skincare routine, start with a lower concentration and gradually increase to avoid irritation, and always apply sunscreen daily to protect your skin from increased sun sensitivity.
Conclusion
Exfoliating actives like AHAs, BHAs, and PHAs offer powerful benefits for achieving smoother, clearer, and more radiant skin. By understanding the unique properties of each type of acid and incorporating them into your skincare routine, you can effectively address your skin concerns and enjoy a healthier complexion. Remember to start slowly, protect your skin from the sun, and listen to your skin’s needs to find the perfect balance for your skincare regimen. With the right approach, exfoliating actives can transform your skin and reveal its natural beauty.

